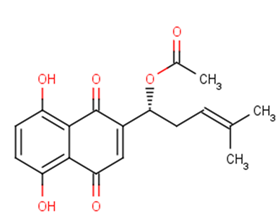
Acetyl shikonin
CAS No. 24502-78-1
Acetyl shikonin( —— )
Catalog No. M18301 CAS No. 24502-78-1
Acetylshikonin exhibits weak cytotoxicity against human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with IC5 of over 2 microM, exhibits the antiangiogenic and antitumorigenic effects by suppressing proliferation and angiogenic factors.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 73 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 125 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 357 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAcetyl shikonin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAcetylshikonin exhibits weak cytotoxicity against human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with IC5 of over 2 microM, exhibits the antiangiogenic and antitumorigenic effects by suppressing proliferation and angiogenic factors.
-
DescriptionAcetylshikonin exhibits weak cytotoxicity against human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with IC5 of over 2 microM, exhibits the antiangiogenic and antitumorigenic effects by suppressing proliferation and angiogenic factors. Acetylshikonin inhibits the generation of NADPH oxidase complex in the activation of respiratory burst of PMNs, but does not directly inhibit the activity of NADPH oxidase already generated. Certain shikonin derivatives(such as Acetyl shikonin) act as modulators of the Nur77-mediated apoptotic pathway and identify a new shikonin-based lead that targets Nur77 for apoptosis induction. Acetylshikonin, shikonin, and alkannin have accelerative effect on the proliferation of granulation tissue in rats. Acetylshikonin has inhibitory effect on the edematous response is due neither to the release of steroid hormones from the adrenal gland nor to the glucocorticoid activity, but probably partly to the suppression of mast cell degranulation and partly to protection of the vasculature from mediator challenge. Acetylshikonin induces apoptosis of hepatitis B virus X protein-expressing human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress.
-
In VitroApoptosis Analysis Cell Line:KB-R5 (oral cancer cell line)Concentration:20 μM, 40 μM, 80 μM Incubation Time:24 h Result:Changed the morphology of the nucleus.Increased apoptosis ratio.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:KB-R5 (oral cancer cell line)Concentration:20 μM, 40 μM, 80 μM Incubation Time:Result:Increased the expression of Beclin-1 and LC3-II and inhibited the expression of p62. However, had no effect on the expression of LC3-I and Vps34.Decreased the expression of p-mTOR, p-PI3K and p-AKT in a concentration-dependent manner.Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:CVA16-induced human rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) cells Concentration: 0.01-5 μM/L (1:1 mix with CVA16 strain TA271)Incubation Time:2 h Result:Reduced CVA16-induced cytopathic effectwith inhibition rates of 80% at the concentration of 0.08 μmol/L.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:L6 (rat skeletal muscle cells) Concentration:0.01 μM, 0.1 μM, 1 μM Incubation Time:2 h Result:Significantly up-regulated phosphorylation of PKCδ.Up-regulates the expression of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4).and PLC-β3.
-
In VivoAnimal Model:D-galactose (D-gal)-induced sub-acuteaging mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD)Dosage:270 mg/kg, 540 mg/kg, 1080 mg/kgAdministration:Intragastrical administration (i.g.); Once daily for 30 days. After D-gal treatment (150 mg/kg; Subcutaneous injection (s.c.); Once daily for 30 days) Result:Decreased levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α.Decreased the content of MDA and increased the activity of SOD. Significantly mitigated D-Gal-induced downregulation of SIRT1 in hippocampal neurons.Significantly inhibited the expression of p53, acetyl-p53, and p21 in mice (all proteins associated with hippocampal aging).Animal Model:CAV16-indeced ICR suckling mice model Dosage:2 mg/kg Administration:Intramuscular injection (i.m.); Single dose. After CVA16 treatment (10[5.5] TCID50/g; Intramuscular injection (i.m.); Single dose )Result:Delayed death of the mice (6 days post-infection and 7 dpi), and eventually resulted in a survival rate of 50% and 70% for the mice in the treatment and prevention groups, respectively (the death of the control mice began at 4 days after infection and all died at 6 days after infection).Animal Model:Obese male C57BL/6J Mice model Dosage:540 mg/kg Administration:Oral gavage (P.O.); Once daily for 8 weeks Result: Reduced body mass index (BMI) and food efficiency in obese mice by 17.1% and 48.2%, respectively.Decreased plasma glucose, CHE, AST and ALT levels by 34.1%, 45.5% and 27.2%, respectively.Significantly inhibited the levels of serum proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β by 49.1%, 41.1% and 45.6%, respectively.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number24502-78-1
-
Formula Weight330.33
-
Molecular FormulaC18H18O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (151.36 mM)
-
SMILESCC(=CCC(C1=CC(=O)C2=C(C=CC(=C2C1=O)O)O)OC(=O)C)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Cucurbitacin S
Cucurbitacin S is isolated from cucurbitaceae with anticancer and anti-inflammatory activities.
-
SMS2-IN-2
SMS2-IN-2 is a potent selective and orally active sphingomyelin synthase 2 (SMS2) inhibitor (IC50s of 100 and 56 μM for SMS2 and SMS1 respectively). SMS2-IN-2 has anti-chronic inflammatory activity.
-
Antalarmin hydrochlo...
CRF1 antagonist



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


